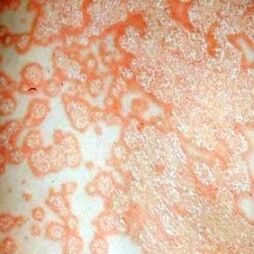
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-infectious skin disease. The disease is recurring. Psoriasis rarely affects joints, nails and mucous membranes. People of all ages are susceptible to psoriasis. According to statistics, the disease has a trend of development in childhood.
Psoriasis is definitely not a chronic infectious disease. Most dermatologists tend to think that psoriasis is a systemic disease. They believe that the disease not only affects specific areas of the skin, but also absorbs almost all the body's systems (endocrine, immune, and nerve) into the pathological process.
From the outside, psoriasis seems to be a mild disease. But in fact, this is not the case. This disease is very dangerous. Death is known in dermatology. If the treatment is not timely or correct, psoriasis can affect the entire body, leading to serious complications. E. g:
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Conjunctivitis
- Mucosal injury
- Flatten and damage the nail plate
- Spontaneous pain
- Muscle atrophy
- Rarely-Heart damage
Generally, psoriasis does not disrupt the patient's normal rhythm of life. The only inconvenience is peeling and inflammation of the skin. Unfortunately, it is impossible to recover from this disease, but it is possible to halt its development or prevent recurrence. For this reason, it is enough to satisfy all the doctor's prescriptions and carry out systematic treatment in the hospital.
Causes of psoriasis
There is no specific cause of the onset of the disease. There are many factors that can lead to the development of psoriasis. There is no clear opinion on one or the other cause of skin disease. There are many versions. Most dermatologists believe that the disease is genetically susceptible. It is impossible to clearly confirm or deny that inheritance is the main reason. In some cases, the entire family suffers from psoriasis.
In other words, we can say this: if a mother has psoriasis, then her offspring will never have to show signs of the disease. But it is impossible to rule out genetic susceptibility. For example, if the grandmother has this disease, it is possible that the grandson will never be diagnosed with psoriasis. The problem of the causes of disease development at the genetic level has not yet been resolved.
According to many dermatologists, the next factor may cause the appearance of psoriasis, which is a disease of the endocrine system. For example, adrenal dysfunction, diabetes, and pituitary dysfunction. In people with endocrine system diseases, the percentage of signs of psoriasis is high. Therefore, there are links between diseases, which have been proved by many examples.
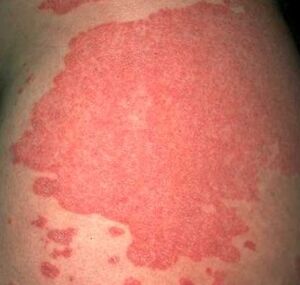
In addition to the above reasons, there are many endogenous factors. E. g:
- Contagious delayed disease, such as tonsillitis. According to statistics, 17% of the patients surveyed believe that psoriasis is the result of complications of angina.
- Chronic infectious pathological processes, such as laryngitis or tonsillitis, can also cause psoriasis.
- Long-term use of certain drugs: interferons, NSAIDs, beta blockers and other drugs.
- It may sound strange, but pregnancy can also lead to the development of psoriasis. In women, there are obvious changes in hormones, which usually trigger the pathological process of dormancy in the body.
- The negative effects of excessive consumption of ultraviolet radiation on the human body cannot be ruled out, that is, prolonged exposure to the hot sun or frequent visits to the solarium.
Naturally, in addition to internal factors, there are many external reasons. For example, skin diseases (dermatitis, fungal disease, pyoderma), mechanical damage to the integrity of the skin, allergic dermatitis.
Interesting facts. Psoriasis is more common in people infected with HIV than in healthy people. It is important to note that women are more susceptible to psoriasis than men. Dry, thinning and sensitive skin is another cause.
You should know that if a person has an immune system disease, this disease often causes psoriasis. Immune diseases are closely related to psoriasis.
There are many causes of psoriasis, but none of them can completely lead to the development of psoriasis.
Types and forms of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a polymorphic disease. According to statistics, people usually only get one type of psoriasis at a time. But in some cases, a person may have multiple forms of psoriasis at the same time. This often happens in dermatological practice, and in this case, one type of psoriasis will be smoothly transmitted to another. Usually, this "rebirth" results in the abrupt cessation of prescribed treatment.
In dermatology, there are two main types of psoriasis: non-pustules and pustules.
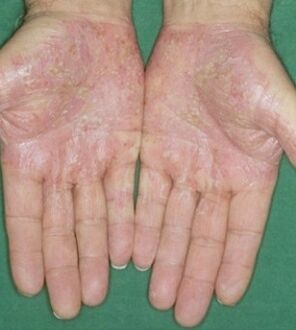
Pustular form-Haircut psoriasis, sole and palm psoriasis (see photo), Zimbabwe psoriasis, ring impetigo. This form of psoriasis is usually divided into systemic and localized. The final pustular psoriasis can occur in any area of the skin. In some cases, pustules form on the plaques of psoriasis vulgaris.
As an example of an independent disease, you can consider allotopic acrodermatitis. Usually, the disease is characterized by pustules on the fingers and toes and damage to the crust of the distal phalanx. Another example of an independent disease of localized psoriasis is pustular psoriasis of the soles of the feet. It is important to note that some dermatologists tend to think of this disease as a form of pustular antiseptic.
Generalized pustular psoriasis includes:
- Herpetic impetigo,
- Psoriasis Tsumbusha,
- Systemic psoriasis.
Generally, men between the ages of 15 and 35 have Zimbabwean psoriasis. This disease is rare in women.
Papular psoriasis occurs suddenly (suddenly). In most cases, it is closely related to other infectious diseases such as tonsillitis. The rash is mainly concentrated on the trunk. Children and adolescents are more susceptible to the disease, and adults are less susceptible.
Herpetiform impetigo is a serious disease that can lead to death. Usually, this disease is characteristic of pregnant women, usually in the second trimester. However, in dermatological practice, there are still very few cases of this disease among men, non-pregnant women and children.
Non-pustular psoriasis. . . In other words, we can say simple psoriasis. This disease is different from other diseases in the stable process. For non-pustular psoriasis, almost the entire body surface is affected. This type includes:
- Erythrodermic psoriasis
- Psoriasis vulgaris, or common or plaque.
Ordinary psoriasis often occurs, and up to 90% of psoriasis patients are vulgar forms of this disease.
Psoriatic erythroderma is a serious disease that usually leads to fatal consequences-death of the patient. For this disease, the temperature regulation function is violated, and the barrier function of the skin is reduced. These pathologies lead to pyoderma or sepsis.
Classification and symptoms of psoriasis
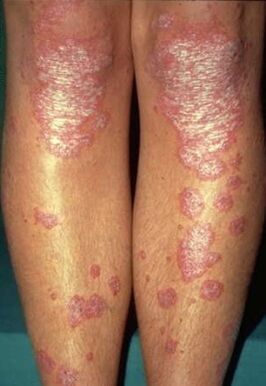
There is no single classification of psoriasis generally accepted by dermatologists. There is still controversy about how to classify this skin disease. Some sources have their own list of forms of psoriasis. Classification of the most common diseases:
- Intestinal psoriasis
- Pustular psoriasis
- Psoriasis Gray Matter
- Mucosal psoriasis
- Exudative psoriasis
- Psoriasis on the soles and palms
- Arthropathy psoriasis
- Trigenic psoriasis
- Psoriasis erythroderma
- Seborrheic psoriasis
- Psoriasis vulgaris
- Pustular Bacteria
- Psoriasis
Arthropathy psoriasisThere are almost no symptoms at first. Patients sometimes only notice slight pain in the joints. As time passed, the pain intensified, becoming sharp and intense. The affected joint is swollen. If the disease is not treated, the joint deforms and its mobility is restricted. Generally, articular psoriasis is usually accompanied by rheumatoid pain. In winter, this disease will increase, that is to say, seasonality is characteristic of this psoriasis.
Pustular psoriasis. . . This situation is not common, accounting for only 1% of the total number of psoriasis patients. In most cases, the rash is symmetrical and located on the soles of the feet and palms. Pustular psoriasis is common and local. The latter form is more common than the former. Systemic pustular psoriasis is difficult. In dermatology, deaths due to sepsis and severe body poisoning are not uncommon.
Psoriasis erythroderma. . . Severe psoriasis is caused by exacerbation of pre-existing psoriasis. This disease may be the result of the deterioration of the underlying disease, or it may be the first time it appears. Usually, 2% of people with this disease will develop secondary erythrodermic psoriasis.
This disease often occurs spontaneously, but cases of psoriasis caused by inappropriate irritant treatment of skin diseases in the acute phase of the disease are not excluded. The patient noticed an increase in pathological foci of skin desquamation, an increase in temperature and detection of dehydration. In dermatological practice, there are death cases in psoriatic erythroderma.
Intestinal psoriasis-Among all forms of psoriasis, the second most common disease is that children and adolescents are more frequently affected. It is characterized by the appearance of a large number of dry, purple and small elements on the skin, which are slightly higher than the unaffected skin surface. The rash is droplets, round or teardrop-shaped. Usually, these elements cover the entire human body, but are most "densely" located on the thighs. In most cases, streptococcal infections can cause teardrop psoriasis. For example, streptococcal pharyngitis, streptococcal pharyngitis.
Psoriasis Gray Matter. . . This disease is characterized by various changes in the appearance of the nail plate, whether on the hands or feet. First, the color of the nails will change, and sometimes the nail beds will be together. The nails become gray, yellow or white. Sometimes dots or small spots appear on the nails even below the nail plate. The nail plate thickens, streaks and brittleness appear. Another clinical manifestation of the disease is thickening of the skin around the nail bed. The difficult outcome of psoriatic onychomycosis is spontaneous nail loss.
Mucosal psoriasis-It is a kind of pustular psoriasis or psoriasis vulgaris. Most commonly, the mucous membranes of the cheeks, tongue, and lips are affected, while the mucous membranes of the genitals and eyes are less likely to be affected. In the form of pustules of psoriasis, the rash is more extensive, large areas of the mucous membrane are affected, and geographical glossitis is noted. In ordinary psoriasis, flat white-gray papules with clear boundaries appear on the mucous membrane, towering on the unaffected surface.
Psoriasis on the soles and palms. . . This disease is a form of localized pustular psoriasis. Usually, this form is chronic and recurrent. In dermatology, sometimes Barbera's psoriasis and plaque psoriasis occur at the same time. Pustules appear on the inner surface of the hands and/or feet. Over time, under the influence of medication, the vesicle pustules dry out. These dry elements then form a dense brown shell.
inter-tri psoriasis. . . The disease is characterized by the appearance of a rash mainly in large skin folds. For example, the hips, the folds between the fingers, the folds in the groin, the armpits and the area under the breast. Interstitial psoriasis is more common in diabetes, VSD (vegetable vascular dystonia), and obese patients who do not follow simple hygiene rules.
Erythematous papules edema foci formed in the folds, erosion and weeping. The important feature of the element of the disease is that the separation of the stratum corneum is obvious along the periphery. Inter-tri psoriasis is very similar to epidermal ringworm, candidiasis or red fungus. It is important to note that the clinical features of candidiasis or dermatophytosis are much brighter and clearer than psoriasis.
Seborrheic psoriasis. . . In terms of its symptoms, seborrheic psoriasis is very similar to seborrheic eczema. Usually, the site of the psoriasis rash is the same as the site of seborrheic eczema. possible:
- Nasolabial fold
- scalp
- Auricle
- Chest area
- Shoulder cap area
When suffering from seborrheic psoriasis, there will be obvious peeling areas on the head. An important feature of the disease is the formation of a psoriasis crown. The skin damage starts from the forehead and spreads smoothly to the scalp. In this simple way, a crown outline appears. It should be noted that dandruff is a warning sign that "says" the development of seborrheic psoriasis.
Usually, red eczema develops behind the auricle, and purulent crusty often develops. The rash that appears locally on the chest and face is characterized by grayish-yellow scales. Psoriasis rash always causes severe itching. It is important to note that seborrheic psoriasis is difficult to diagnose because it is often confused with seborrhea.
Exudative psoriasis. . . This type of psoriasis is more common in children and the elderly. Patients with abnormal endocrine and immune systems are at high risk of developing this disease. Exuding psoriasis usually affects the healthy skin of people who are overweight or have diabetes.
This disease is characterized by the accumulation of excessive exudate in the papules, which gradually penetrates into the surface, forming a pale yellow crust. If the crust is removed, the leaking and oozing surface will be exposed. The scales will dry up over time and stack on top of each other, thus forming a fairly dense mass.
The main feature of exudative psoriasis is the clear location of the pathological focus. Generally, the lower extremities and large folds are most affected. The rash gives the strongest itching and burning sensation. The clinical manifestations of this disease are sharp and acute.
Psoriasis vulgaris. . . It has different names in different sources. For example, plaque, ordinary, simple. This type of psoriasis ranks first in terms of prevalence-it is observed in almost 90% of psoriasis patients. The disease usually starts severe enough. The first symptoms appeared almost immediately.
Psoriasis vulgaris is characterized by the appearance of typical components, which are slightly higher than the unaffected areas of the skin. The rash is inflamed, red, and hot to the touch. The elements are thickened and covered with a silver-white, scaly dry film (skin) that can easily fall off.
You should know that gray skin is easy to remove, which can cause damage to the lower layer of the pimples, which contains a lot of small blood vessels. This usually results in a slight undercut. The affected lesions in skin diseases are called psoriatic plaques.
Such plaques have a tendency to coalesce, which causes their size to increase. As time passed, a plaque plate was formed, which has a unique name-"Paraffin Lake". Psoriasis outbreaks with ordinary psoriasis are highly prone to exfoliation. Treatment is long-term and requires hospitalization.
Pustular Bacteria. . . According to statistics, this disease mainly occurs in young people (from 20 years old) and middle-aged people (under 50 years old). The exact cause of pustular antiseptic has not been determined. There is a hypothesis that this disease develops in the context of a strong and long-term allergic reaction associated with infectious lesions. For example, dental caries, tonsillitis or tonsillitis.
An outbreak of psoriasis can affect the skin of the palms and soles of the feet. Pustular fungicides are chronic and recurrent. The first focus appears on the palm, then on the center, and if it appears on the sole, it appears on the arch of the foot. The size of the primary psoriasis is very small, no more than the size of the needle. Over time, the pustules dry out and form a layered crust. The patient felt severe itching and soreness in the affected area.
The paroxysmal course of the disease is characteristic of pustular fungicides. At the same time, inflammation occurs in all areas affected by psoriasis. Psoriasis foci gradually increased, and after a few weeks, almost the entire surface of the palm or sole of the foot was pulled into the pathological process. Usually, the pustular bacteria will persist for several years and keep recurring.
Nutrition for psoriasis
Patients with psoriasis only need to follow their eating habits and observe the basic principles of proper nutrition. The main task of the diet is to maintain a normal acid-base balance. But it is important to note that the alkaline background of the human body should be slightly better than the acidic background.
Naturally, the balance of the body depends on the food that people with psoriasis eat every day. For everyone suffering from this disease, it is important to know that products that should form alkalis in the body account for 70% of the daily diet. Form acid-not more than 30%. In simple terms, it can be said that the product that produces alkali must consume 4 times more than the product that produces acid.
List of products that form alkali in the body:
- All vegetables except rhubarb, pumpkin and Brussels sprouts. It is important to remember that potatoes, peppers, eggplants and tomatoes are strictly prohibited.
- Fruit should not be excluded. The main thing is not to use plums, cranberries, raisins and blueberries. It is worth noting that bananas, melons and apples should not be consumed at the same time as other foods.
- Be sure to drink fresh vegetable juices from carrots, beets, parsley, celery and spinach.
- You can eat juices made from grapes, pineapples, pears, oranges, papaya and grapefruit, mangoes, lemons and apricots every day. It is important to add lemon juice to food.
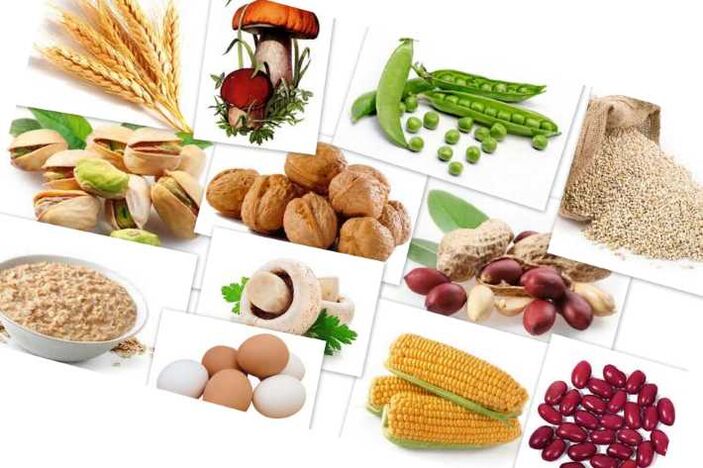

List of foods forbidden to eat for psoriasis patients (acid form):
- You should completely eliminate or reduce the consumption of foods containing starch, fat, sugar and oil. Generally, these foods include the following foods: potatoes, beans, cream, cheese, grains, meat, dried peas. The imbalance in the daily intake of these products inevitably leads to the onset of acid reactions in the blood. The result is a decline in happiness.
- Properly balanced food is important. It is forbidden to eat multiple foods at the same time. For example, meat foods should not be mixed with foods with high sugar content, as well as candies and starches.
- It is important to limit sugar intake. Preservatives, vinegar, dyes and various food additives should be added as little as possible in the diet.
- The main point is that the consumption of alcohol and alcoholic beverages must be completely eliminated.
Every patient with psoriasis should remember that the right diet is an important condition for the treatment of this disease. Stew or boil must be used instead of frying. It is necessary to eat mildly processed foods.
Psoriasis treatment
The treatment of psoriasis should be carried out in the hospital during the exacerbation period, and in the outpatient-during the remission period. Diet is the focus of treatment. Fasting days are useful.
In addition to diet and specialized treatment, careful monitoring of skin hygiene is also important. When washing, it is best to use tar soap or baby soap. You should fry with celandine, pansies or hop soup as often as possible.
If there are no contraindications, you can try to treat psoriasis and folk remedies. Don't experiment and self-medicate. Only the doctor has the right to suggest which folk remedies are useful and necessary.
List of safe and effective psoriasis ointments:

- A pack of butter (but not spreading) butter should be placed in a pot (10 g) containing crushed propolis. After boiling for 15 minutes, put it on fire and simmer. After that-the mixture must be filtered thoroughly and allowed to cool. Only store this medicine in the refrigerator. How to use-Rub into the affected area several times a day.
- In a clay dish, it is necessary to grind the flowers of St. John's wort (20 g), celandine root, propolis, and marigolds (10 g). Vegetable oil is added to the resulting mixture. Store in a cool place away from direct sunlight. Usage-Lubricate psoriasis 3 times a day.
- Boil a liter of white wine for half an hour and cook sea fish with gallbladder and scales on a fairly low flame. They weigh more than three kilograms. Cool, strain, and then add a cup of olive oil. How to use-Wash the affected area thoroughly with egg soap and dry it. After that, lubricate the components with this mixture. The treatment process continues until the drug is used up.
- Mix equal parts of celandine powder and petroleum jelly (by weight) thoroughly. Application method-apply the ointment to the thin layer on the rash and leave it for three days. After that, you need to take a short rest of about 4 days. Treat until the psoriasis disappears completely.
- Add a tablespoon of vegetable oil to the hard-boiled eggs (2 pcs). The mixture was whipped again, and then acetic acid (40 g) was introduced. Store the ointment in a jar with a tight-fitting lid. Application method-once a day, preferably at night to treat psoriasis outbreaks.
- An equally effective and common treatment for psoriasis is to cure sludge. The mud must be heated to 38 degrees and then applied to the affected skin. This process should be done at night, preferably before going to bed. After 30 minutes, remove the dirt with warm water. It is important to remember that all rashes should be treated with saline after the dirt has appeared. The body should dry out and the excess salt should fall off. No need to wash or moisturize your skin, you need to go to bed. And only in the morning, can the cream be used to lubricate the psoriasis ingredients. The recommended course is 20 programs (every other day).
Regardless of the popular treatment of psoriasis, you must consult with the attending dermatologist.